Gastrointestinal Bleeding Treatment Specialist Q&A
Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur anywhere in the digestive tract, ranging from minor to severe levels. If left untreated, it can be life-threatening, which is why it needs urgent medical attention. GI bleeding may be a sign of underlying conditions such as peptic ulcers, hemorrhoids, gastritis, and diverticulitis. Dr. Usha Rani K. Reddy at Reddy Urgent Care provides assessment to detect and treat GI bleeding promptly. For more information, contact us. Walk-in visits are welcome. We have convenient locations to serve you in Bixby Knolls Long Beach, Downtown Long Beach, and Paramount, CA.
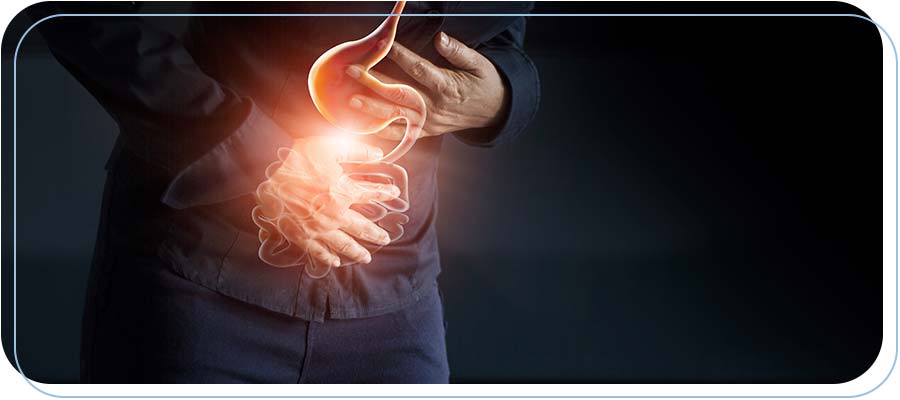
Table of Contents:
What is gastrointestinal bleeding?
What is the most common cause of GI bleeding?
What are the symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding?
How is gastrointestinal bleeding diagnosed?
How is gastrointestinal bleeding treated?
Gastrointestinal bleeding can be caused by a number of conditions ranging in severity, but is typically noticed due to a presence of blood in the stool. So, while there is a chance that seeing blood in the stool is indicative of a very mild condition, it is always highly recommended that patients seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Gastrointestinal bleeding is typically indicative of a disorder within the digestive system, such as ulcers, reflux, or cancer, occurring in any part along the gastrointestinal tract, which runs from the mouth all the way down to the anus. The bleeding will likely be present in the stool or in vomit, but is not always clearly blood due to a dark hue that it can sometimes take on, particularly in the stool. Blood that is present in the stool due to gastrointestinal bleeding is typically described as looking black or tar-like. Gastrointestinal bleeding can often just be a mild and maybe ongoing condition, but there are many cases when spontaneous bleeding can be indicative of a severe, life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
There are many different health conditions that can cause GI bleeding, with different causes leading to bleeding from the upper GI tract versus the lower GI tract.
The most common conditions that lead to bleeding from the upper GI tract include:
– Cancer (pancreatic, liver, and esophageal)
– Chronic acid reflux
– Gastritis
– Peptic ulcers
The most common conditions that lead to bleeding from the lower GI tract include:
– Anal or colorectal cancer
– Anal fissures
– Polyps within the colon
– Diverticulitis and diverticulosis
– Rectal ulcers
– Hemorrhoids
Crohn’s disease and gastrointestinal stromal tumors can cause bleeding both in the upper and lower GI tract. Of all of the mentioned potential causes for GI bleeding, peptic ulcers are the most common cause, which develop as open sores along the inside lining of the upper part of the small intestine and stomach.
The presence of blood in or on the stool is the most well-known symptom of gastrointestinal bleeding, but there are several other symptoms that commonly occur as a result of gastrointestinal bleeding, including:
– Cramping within the abdomen
– Shortness of breath
– Becoming pale in appearance
– Increased weakness and general fatigue or tiredness
– Vomit that contains blood
Some symptoms that are often associated with acute and more severe gastrointestinal bleeding include:
– Quickening pulse (can feel like anxiety or heart fluttering)
– Faintness or dizziness
– Difficulty with urinating
– Insufficient blood flow to the organs resulting in shock
Physicians can diagnose gastrointestinal bleeding through a number of different tests, which will be chosen depending on the other symptoms that are present. Initial signs for GI bleeding can include having a blood test to check for anemia, or providing a stool sample to have checked for signs that there is blood in the stool. Diagnostic imaging tests such as CT scans or GI x-rays may be required to provide the health care provider with a visual of the intestines to check for signs of a bleed or other potential conditions that could be causing the symptoms. Another diagnostic option includes an upper endoscopy, which is the insertion of a camera with a light to examine the upper part of the small intestine or a balloon enteroscopy, which is similar but uses tiny balloons to inflate the hard to reach areas within the small bowel to allow for easier visibility and examination. Colonoscopies and sigmoidoscopies are used to examine the lower portion of the GI tract, with the endoscope being inserted through the anus rather than the esophagus.
The method of treatment for gastrointestinal bleeding depends on the cause of the bleed, with some conditions being able to be treated just through medication, and some requiring surgical procedures. Some conditions can be treated using more than one method, so the method chosen may depend on the severity of the condition or the exact location of the cause along the GI tract. For example, peptic ulcers can be treated both through an upper endoscopy or through the removal of the polyps during a colonoscopy.
For more information, contact us. We have convenient locations to serve you. We serve patients from Bixby Knolls Long Beach CA, Downtown Long Beach CA, Paramount CA, Lakewood CA, Rossmoor CA, Carson CA, Bellflower CA, Lynwood CA, Norwalk CA, and surrounding areas.
Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews